| The verb be | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Infinitive form | be | ||
| Present simple: | + | I am, I'm You are, You're He/She/It is, He/She/It's | We are, we're You are, you're They are, they're |
| ? | Am I? Are you? Is he/she it? | Are we? Are you? Are they? | |
| - | I am not, I’m not You are not, You aren’t, You're not He/She/It is not, He/She/It isn’t, He's not | We are not, We aren’t, We're not You are not, You aren’t, You're not They are not, They aren't, They're not | |
domingo, 27 de octubre de 2019
NOVENO
REVISE LA ESTRUCTURA DEL VERBO TO BE EN PRESENTE
DECIMO
MIRE LOS GRÁFICOS Y PRACTIQUE EL USO DEL PASADO EN INGLES
EXAMPLE:
WHO INVENTED THE TELEVISION ?
PHILO TAYLOR INVEBTED THE TELEVISION
PRIMERO
MATERIA : INGLES
REVISE LA INFORMACION
LEA LAS ORACIONES Y USO DEL PRESENTE PERFECTO
Unfinished Actions
1: We use this tense when we want to talk about unfinished actions or states or habits that started in the past and continue to the present. Usually we use it to say 'how long' and we need 'since' or 'for'. We often use stative verbs.
We use 'since' with a fixed time in the past (2004, April 23rd, last year). The fixed time can be another action, which is in the past simple (since I was at school, since I arrived).
REVISE LA INFORMACION
LEA LAS ORACIONES Y USO DEL PRESENTE PERFECTO
Unfinished Actions
1: We use this tense when we want to talk about unfinished actions or states or habits that started in the past and continue to the present. Usually we use it to say 'how long' and we need 'since' or 'for'. We often use stative verbs.
- I've known Karen since 1994.
- She's lived in London for three years.
- I've worked here for six months.
We use 'since' with a fixed time in the past (2004, April 23rd, last year). The fixed time can be another action, which is in the past simple (since I was at school, since I arrived).
- I've known Sam since 1992.
- I've liked chocolate since I was a child.
- She's been here since 2pm.
- I've known Julie for ten years.
- I've been hungry for hours.
- She's had a cold for a week.
miércoles, 23 de octubre de 2019
TERCERO 23 DE OCTUBRE
INGLES:
REPASE EL VOCABULARIO DE LA PAGINA 20 INCLUIDO LAS COLLOQUIAL EXPRESSIONS
INGRESE AL LINK Y REPASE LOS VERBOS
https://es.slideshare.net/nalanalan/irregular-verbs-with-pictures-3134651
LENGUA Y LITERATURA
REALIZAR EL PLAN LECTOR
REPASE EL VOCABULARIO DE LA PAGINA 20 INCLUIDO LAS COLLOQUIAL EXPRESSIONS
INGRESE AL LINK Y REPASE LOS VERBOS
https://es.slideshare.net/nalanalan/irregular-verbs-with-pictures-3134651
LENGUA Y LITERATURA
REALIZAR EL PLAN LECTOR
segundo 23 de octubre
LENGUA Y LITERATURA
REVISE EL LINK A CONTINUACION SOBRE EL TEMA DE LA NOVELA REALISTA
http://andrealanovelarealista.blogspot.com/2016/
INGLES
REPASE EL VOCABULARIO DE LA PG 20 DEL LIBRO- COLLOQUIAL EXPRESSIONS
REVISE EL LINK A CONTINUACION SOBRE EL TEMA DE LA NOVELA REALISTA
http://andrealanovelarealista.blogspot.com/2016/
INGLES
REPASE EL VOCABULARIO DE LA PG 20 DEL LIBRO- COLLOQUIAL EXPRESSIONS
primero 23 de octubre
revise la información de refuerzo para esta semana
Practique las siguientes oraciones
siga la estructura de presente perfecto en ingles, y complete las oraciones.
use los AUXILIARES have o has de acuerdo al sujeto.

Practique las siguientes oraciones
siga la estructura de presente perfecto en ingles, y complete las oraciones.
use los AUXILIARES have o has de acuerdo al sujeto.
Put the verbs into the correct form (present perfect simple).
- I (not / work) today.
- We (buy) a new lamp.
- We (not / plan) our holiday yet.
- Where (be / you) ?
- He (write) five letters.
- She (not / see) him for a long time.
- (be / you) at school?
- School (not / start) yet.
- (speak / he) to his boss?
- No, he (have / not) the time yet.
LENGUA Y LITERATURA
realice el plan lector
EMPRENDIMIENTO Y GESTIÓN
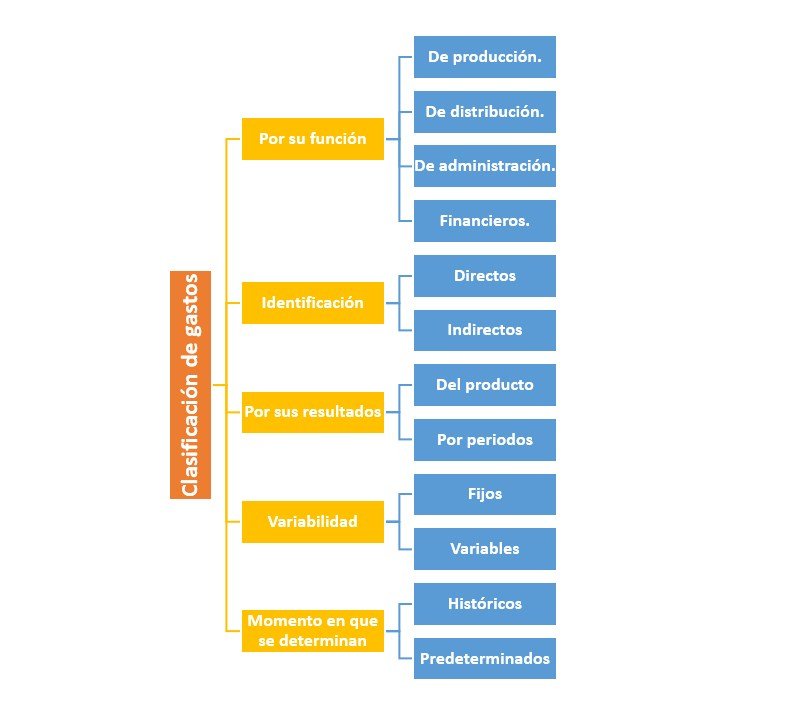
Fórmula del punto de equilibrio
La fórmula para calcular el punto de equilibrio más utilizada es la de unidad, a partir de esta se pueden calcular la cantidad de unidades que necesitamos vender para no ir a pérdida, así también la cantidad de dinero en ventas que necesitamos para llegar al punto de equilibrio:

Fórmula para calcular el punto de equilibrio por unidad
Los elementos que se necesitan en esta fórmula son:
- Costos fijos: Aquellos que independientemente del nivel de producción, siempre están presentes. Por ejemplo: sueldo de empleados.
- Precio de venta unitario: El precio en el que es vendida cada unidad.
- Costo variable unitario: Aquel que varía según el nivel de producción. Por ejemplo: la materia prima.
decimo 23 de octubre
practique el tiempo pasado con las siguientes oraciones
bueque el pasado de cada verbo que esta en parentesis
Past:
Yesterday, I took my young brother to the park and bought him an ice-cream. We kicked around a football, laughed and talked for hours.
Yesterday, I took my young brother to the park and bought him an ice-cream. We kicked around a football, laughed and talked for hours.
Simple Past Tense Exercise: change the verbs in brackets to the simple past. Be careful with spellings.
- 1) They all (go) ___ shopping.
- 2) I never (imagine) ____ I would see you here.
- 3) We (book) ___ two tickets for the show.
- 4) He (collect) ___ his children from school.
- 5) Were you (frighten) ___ of the dark when you were young?
- 6) Who (eat) ___ my chocolate?
- 7) I (feel) so tired that I went straight to bed.
- 8) We (grow) ___ this tree from a seed.
- 9) She (lose) ___ her way home.
- 10) He thought I (steal) his umbrella.
noveno 23 de octubre
revise el blog como refuerzo para esta semana

Present simple, third person
Present simple is used when talking about a regularly occurring action, something that is general knowledge or an unchanging condition.
EXAMPLES:
I walk to work on Mondays.
Some people put milk in their tea.The sun is brighter than the moon
Some people put milk in their tea.The sun is brighter than the moon
In present simple, the verb changes only in third person singular (he, she, it, a person, a thing), where it gets the suffix -s or -es.
EXAMPLES:
run -> Emily runscatch -> Sam catches butterflies
The -es suffix is used when the verb ends in the letters ss, sh, ch, x or z.
EXAMPLES:
misses, not misss
fixes, not fixs
fixes, not fixs
example:
Emily runs in the park.

octavo 23 de octubre
refuerzo para esta semana
revise el link con los adjetivos
https://www.esolcourses.com/content/exercises/grammar/adjectives/personality/words-for-describing-personality.html
revise el link con los adjetivos
https://www.esolcourses.com/content/exercises/grammar/adjectives/personality/words-for-describing-personality.html
domingo, 13 de octubre de 2019
Actividades 13de octubre
A todos los estudiantes por favor realizar las actividades de acuerdo a la agenda.
Rogamos que la situación actual que vivimos en el país pueda ser superada
Rogamos que la situación actual que vivimos en el país pueda ser superada
OCTAVO
INGLÉS LIBRO DE TRABAJO ES DECIR LA SEGUNDA PARTE DEL TEXTO PAGINAS 14-15
NOVENO
INGLÉS LIBRO DE TRABAJO ES DECIR LA SEGUNDA PARTE DEL TEXTO PAGINAS 15
DÉCIMO
INGLÉS Solve pag. 19 QUIZ TIME Ingrese al blog y registre su asistencia. Repasar la canción de la plataforma Lyricstraining I’m still standing
PRIMERO BGU
INGLÉS REPASE 20 VERBOS APRENDIDOS Repasar la canción de la plataforma Lyricstraining I’m still standing
EMPRENDIMIENTO Y GESTIÓN Resuelva el ejercicio de la página 30
SEGUNDO BGU
INGLÉS REVISE EL CUADRO DE REFLECT ON GRAMMAR DE LA PAG 13 – PASELOS AL CUADERNO
EDUCACIÓN ARTÍSTICA Realice la actividad desarrollo mis destrezas página 27
TERCERO BGU
INGLÉS
|
NOTA: ENTRE AL WWW.LYRICSTRAINING.COM Y REPASE LA CANCIÓN
martes, 8 de octubre de 2019
TERCERO
REVISE LA INFORMACION Y PASE AL CUADERNO
FECHA DE 06 DE OCTUBRE
CON EL TEMA
PAST PERFECT
DECIDE, PAST PERFECT
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I had decided | I hadn't decided | Had I decided? |
| You had decided | You hadn't decided | Had you decided? |
| She had decided | She hadn't decided | Had she decided? |
| We had decided | We hadn't decided | Had we decided? |
| They had decided | They hadn't decided | Had they decided? |
FORMING THE PAST PERFECT
The Past Perfect tense in English is composed of two parts: the past tense of the verb to have (had) + the past participle of the main verb.
| Subject | had | past participle | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | |||||
| She | had | given | |||
| Negative | |||||
| She | hadn't | asked. | |||
| Interrogative | |||||
| Had | they | arrived? | |||
Interrogative Negative
| |||||
| REALICE ORACIONES EN PAST PERFECT CON LOS VERBOS SIGUIENDO EL EJEMPLO DE LA TABLA DE ARRIBA * FORGIVE *COME * START MATERIA: LENGUA Y LITERATURA REVISE EL LINK https://prezi.com/1k2d9p2ku0kt/mandalas-literarias/ REALICE LA ACTIVIDAD https://www.modelopresentacion.com/como-hacer-un-discurso.html | |||||
SEGUNDO
SEGUNDO 06- DE OCTUBRE REFUERZO
REVISE EL MATERIAL Y REALICE LA ACTIVIDAD
MATERIA: LENGUA Y LITERATURA
SIGA EL MODELO DEL MENTEFACTO A CONTINUACIÓN, PARA QUE REALICE UN MENTEFACTO COMO ACTIVIDAD EN CLASE CON FECHA 06-10-2019
CON EL TEMA PRINCIPAL: "EL DEPORTE COMO PARTE DE LA SALUD"
https://www.lifeder.com/mentefacto/
MATERIA: INGLÈS
REVISE EL LINK CON LA INFORMACIÓN Y REALICE LA ACTIVIDAD COM0 TRABAJO EN CLASE FECHA 06-10-2019
TEMA: PRESENT PERFECT
The past participle, for regular verbs, is the same as the past simple.
EXAMPLE WITH THE VERB " LIVE"
REALICE LOS EJEMPLOS COMO LA TABLA DE ARRIBA CON LOS VERBOS
MATERIA: LENGUA Y LITERATURA
SIGA EL MODELO DEL MENTEFACTO A CONTINUACIÓN, PARA QUE REALICE UN MENTEFACTO COMO ACTIVIDAD EN CLASE CON FECHA 06-10-2019
CON EL TEMA PRINCIPAL: "EL DEPORTE COMO PARTE DE LA SALUD"
https://www.lifeder.com/mentefacto/
MATERIA: INGLÈS
REVISE EL LINK CON LA INFORMACIÓN Y REALICE LA ACTIVIDAD COM0 TRABAJO EN CLASE FECHA 06-10-2019
TEMA: PRESENT PERFECT
The present perfect is formed from the present tense of the verb have and the past participle of a verb.
We use the present perfect:
- for something that started in the past and continues in the present:
They've been married for nearly fifty years.
She has lived in Liverpool all her life.
- when we are talking about our experience up to the present:
I've seen that film before.
I've played the guitar ever since I was a teenager.
He has written three books and he is working on another one.
We often use the adverb ever to talk about experience up to the present:
and we use never for the negative form:My last birthday was the worst day I have ever had.
Have you ever met George?
Yes, but I've never met his wife.
The past participle, for regular verbs, is the same as the past simple.
| Infinitive | Past Simple | Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| work live watch | worked lived watched | worked lived watched |
| Present Perfect | ||
|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Question |
| I have lived You have lived He has lived She has lived It has lived We have lived You have lived They have lived | I haven't lived You haven't lived He hasn't lived She hasn't lived It hasn't lived We haven't lived You haven't lived They haven't lived | Have I lived? Have you lived? Has he lived? Has she lived? Has it lived? Have we lived? Have you lived? Have they lived? |
* DO
*HAVE
*PLAY
PRIMERO
PRIMERO 06 DE OCTUBRE REFUERZO
MATERIA: INGLES
PASAR AL CUADERNO CON FECHA 06 DE OCTUBRE COMO ACTIVIDAD EN CLASE
Simple Present Forms
The simple present is just the base form of the verb. Questions are made with do and negative forms are made with do not.
- Statement: You speak English.
- Question: Do you speak English?
- Negative: You do not speak English.
In the third person singular, -s or -es is added. Questions are made with does and negative forms are made with does not.
- Statement: He speaks English.
- Question: Does he speak English?
- Negative: He does not speak English.
FUTURE
FORM Will
[will + VERB]
Examples:
- You will help him later.
- Will you help him later?
- You will not help him later.
| Subject | will | infinitive without to |
|---|---|---|
| Affirmative | ||
| I | will | go |
| I | shall | go |
| Negative | ||
| They | will not | see |
| They | won't | see |
| Interrogative | ||
| Will | she | ask? |
| Interrogative negative | ||
| Won't COMPLETE LAS ORACIONES
Complete the sentences in the future simple (will).
MATERIA: LENGUA Y LITERATURA
Características del ensayo argumentativo:
Por ser un texto cuya finalidad es dar a conocer el planteamiento del autor el ensayo argumentativo es un tipo de texto libre que transita los géneros discursivos de la descripción, la exposición y la argumentación. Sus principales características son:
Tema libre: la temática elegida para tratar en el ensayo depende de los intereses del autor, sus conocimientos y experiencia en la materia así como su pasión por el mismo.
Por ello el tema es siempre de libre elección para el autor. Claro que en casos de ensayos asignados previamente por un docente, quizás no habrá mucha libertad a la hora de elegir el tema, pero si en el modo de abordarlo.
Lenguaje formal: siempre al momento de redactar un texto académico y en especial un ensayo con argumento, el lenguaje debe ser formal, respetando las formas estructurales de la gramática y sin hacer uso de coloquialismos que dificulten la lectura.
Argumentos: la argumentación es la clave del ensayo argumentativo. Consiste en la sustentación de las ideas expresadas con el apoyo de planteamientos sólidos que permitan convencer al lector.
Los argumentos pueden valerse de citas textuales de otros autores, siempre respetando las normas de citado y los derechos de autor. Incluso siempre es recomendable que existan citas que permitan apoyar las ideas del autor.
Coherencia: la coherencia es parte fundamental de todo texto escrito. Se trata de mantener una ilación acorde entre las ideas que faciliten la lectura y comprensión por parte del lector.
Para que un texto sea coherente hay que mantener orden a la hora de esgrimir los argumentos y a su vez construir correctamente las oraciones, respetando la gramática y la ortografía.
Extensión: la extensión de todo ensayo suele ser igual o superior a las 5 cuartillas. De ser más corto no se trata propiamente de un ensayo si no de un análisis, un artículo de opinión, un papel de trabajo o de cualquier otro tipo de ejercicio del pensamiento.
Si bien la extensión del ensayo argumentativo es variable y depende de los planteamientos del autor, la temática abordada y las referencias citadas, suelen ser superiores a las cinco cuartillas, pues se requiere de un espacio amplio de texto para poder desarrollar las ideas.
MATERIA: EMPRENDIMIENTO Y GESTIÓN
 | they | try? |
DECIMO
DECIMO 06 DE OCTUBRE REFUERZO
PASAR AL CUADERNO CON FECHA 06 DE OCTUBRE COMO ACTIVIDAD EN CLASE
REVISE LOS VERBOS EN PARÉNTESIS Y CAMBIELOS A PASADO
ESCRIBA LA ORACIÓN COMPLETA EN PASADO
Put the verbs into the simple past:
- Last year I (go) to England on holiday.
- It (be) fantastic.
- I (visit) lots of interesting places. I (be) with two friends of mine .
- In the mornings we (walk) in the streets of London.
- In the evenings we (go) to pubs.
- The weather (be) strangely fine.
- It (not / rain) a lot.
- But we (see) some beautiful rainbows.
- Where (spend / you) your last holiday?
ESCRIBA EL PASADO DE LOS VERBOS A CONTINUACIÓN
Write the past forms of the irregular verbs.
| Infinitive | Simple Past | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. |
meet
|
.
|
| 2. |
drive
|
.
|
| 3. |
speak
|
.
|
| 4. |
put
|
.
|
| 5. |
write
|
.
|
| 6. |
sing
|
.
|
| 7. |
do
|
.
|
| 8. |
sit
|
.
|
| 9. |
stand
|
.
|
| 10. |
run
|
.
|
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)
